Ion-Exchange Desalination Battery with Reversible Chloride Capture
- Journal
- ACS Energy Letters
- Year
- 2024
- Link
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsenergylett.4c00904 1254회 연결
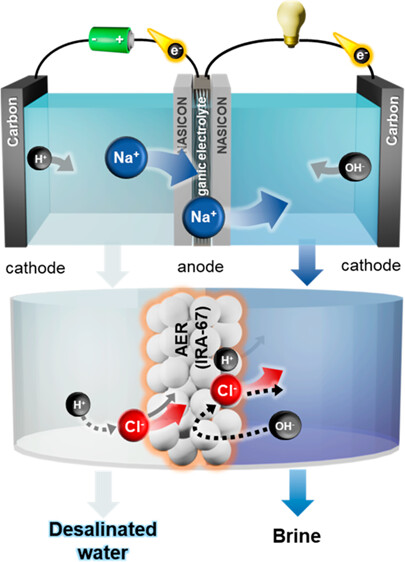
Seawater desalination technology aims to address the global water shortage resulting from climate change. However, for a viable solution, it is imperative to utilize renewable energy sources without carbon emissions. Desalination batteries represent a promising water–energy nexus technology; nonetheless, the limited reversibility of Cl– capture hinders their practicality. In this study, an ion-exchange desalination battery (IEDB), composed of an anion-exchange resin (AER) column filled with IRA-67 and a seawater battery (SWB), concurrently stores energy and desalinates seawater. During the charging of the SWB, Cl– is adsorbed on IRA-67, leading to seawater desalination. Subsequently, the Cl– is desorbed during discharge, automatically regenerating IRA-67 through the chemical potential. The proposed IEDB demonstrates 358 mL of seawater desalination with 1.48 Wh of energy storage through repetitive charge–discharge. This result secures the stability of desalination batteries, which is essential for an efficient water-energy nexus.