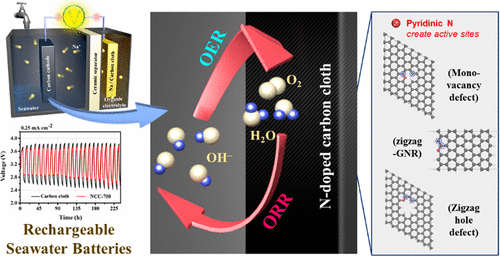
Pyridinic-Nitrogen-Containing Carbon Cathode: Efficient Electrocatalyst for Seawater Batteries
- Journal
- ACS Appl. Energy Mater.
- Vol
- 3
- Page
- 1602-1608
- Year
- 2020
- Link
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsaem.9b02087 953회 연결
Sodium-metal-based seawater batteries (SWB) are considered an attractive energy storage system because of the cost-effective nature of Na+ ions. However, the high overpotential and low power output caused by the limitations of the cathode material have impeded their commercialization. To overcome these injurious issues, herein we report the enhanced oxygen reduction reaction (ORR)/oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activities of SWBs using a well-controlled N-doped carbon cloth as a cathode current collector. The resulting electrochemical performance reveals that the presence of pyridinic-N prepared by pyrolysis at 700 °C is related to the enhanced electrocatalytic activity toward the OER and ORR and the improved electrochemical behavior of the SWB. At a current density of 0.25 mA cm–2, the SWB with a pyridinic-N-containing cathode shows a lower overpotential of 0.84 V and a higher power density of 9.66 mW cm–2, which are significantly better than those of graphitic-N-dominated carbon cathodes. Furthermore, the in-depth density functional theoretical (DFT) calculations support our claim that pyridinic-N-doping at the zigzag edges or monovacancy defects of the carbon structure are responsible for the enhancement in the electrochemical performance of the SWB, and the carbon atoms close to pyridinic-N are the main active sites.