Redox-Additive-Enhanced High Capacitance Supercapacitors Based on Co2P2O7 Nanosheets
- Journal
- Advanced Materials Interfaces
- Vol
- 4
- Page
- 1700059
- Year
- 2017
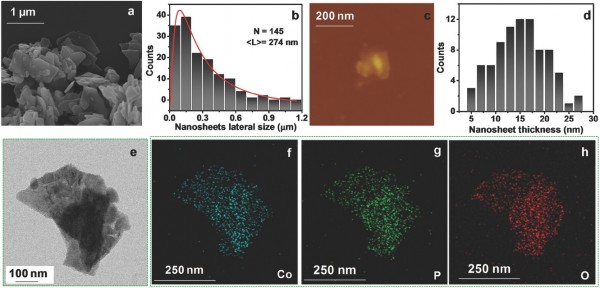
Cobalt pyrophosphate (Co2P2O7) has emerged as an attractive material due to its high specific energy and redox behavior of cobalt, however, problems associated with its poor specific capacitance and cyclic stability have prevented its realization. Here, the authors circumvent these problems by hydrothermally synthesizing layered Co2P2O7 nanosheets (lateral size ≈300 nm with average thickness ≈15 nm) and demonstrate significant improvements in the specific capacitance of Co2P2O7 nanosheets by the addition of a redox additive (K3Fe(CN)6) into KOH aqueous electrolyte. Without the additive, Co2P2O7 nanosheets show specific capacitance of 286 F g−1 at 1 A g−1 current density. However, by introducing 0.1 m redox additive to the electrolyte the specific capacitance of Co2P2O7 nanosheets increased more than twofolds (580 F g−1 at 1 A g−1 current density), which is due to the improvement of redox reactions at the electrode/electrolyte interface and the enhanced ionic conductivity of electrolyte. Furthermore, with the redox additive, Co2P2O7 nanosheets show an excellent cyclic stability (96% retention of its initial capacitance) and coulombic efficiency (99% retention) up to 5000 cycles at high current density 10 A g−1.