Atomic structural and electrochemical impact of Fe Substitution on nano porous LiMnPO4
- Journal
- Journal of Power Sources
- Vol
- 320
- Page
- 59-67
- Year
- 2016
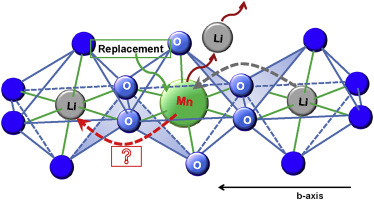
The atomic structural and electrochemical properties of Fe substituted nano porous LiMn1-xFexPO4 (x = 0–0.8) composites are investigated and compared. X-ray scattering method is used for atomic structural investigation. Rietveld refinement shows that all Fe substituted composites have the same olivine structure (Pnma) with lithium occupying octahedral 4a sites, Fe2+ replacing Mn2+ at the octahedral 4c sites. The a, b, c parameters and cell volume decrease with the addition of Fe2+. When the nano porous LiMn1-xFexPO4 composites are evaluated as cathode materials in lithium cells at room temperature, x = 0.6, and 0.8 resulted in the best overall electrochemical performance, exhibiting stable cycling and high discharge capacities of 149 and 154 mA h g−1, respectively. The composites with above x = 0.4 show a fast lithium ions transfer with high electronic conductivity because Fe transition metal substitution reduce the partly occupation of Mn in the M1 (LiO6) sites and thereby Mn block the lithium ion diffusion pathway. We here firstly find the antisite defect in the high Mn content in porous LiMn1-xFexPO4 composites.