Electrochemical characterization of micro-rod β-Na0.33V2O5 for high performance lithiumion batteries
- Journal
- Electrochimica Acta
- Vol
- 193
- Page
- 160-165
- Year
- 2016
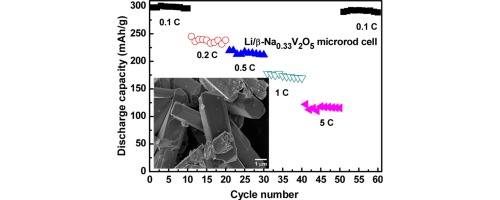
High-purity micro-rod β-Na0.33V2O5 particles 2–5 μm in width and 3–10 μm in length are prepared by the chemical switch method. Electrochemical characterization demonstrates that micro-rod β-Na0.33V2O5 as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries provides high discharge capacity, good rate-capability, and cyclic stability. It delivers high discharge capacities of 297, 245, 220, and 178 mAh g−1 at current densities of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1 C-rate, respectively. The capacity fading rate is less than 1% per cycle, with high volumetric discharge capacities (504 mAh cm−3 at 0.1C and 301 mAh cm−3 at 1 C). Scanning electron microscopy images of the micro-rods during cycling indicate that they have excellent crystal structural reversibility in the voltage range of 1.5–4.0 V. These superior electrochemical properties are attributed to the tunneled crystal structure and internal pores formed by crystal defects in the micro-rods.