New Chemical Route for the Synthesis of B-Na0.33V2O5 and its Fully Reversible Li Intercalation
- Journal
- ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
- Vol
- 7
- Page
- 7025-7032
- Year
- 2015
- Link
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsami.5b01260 688회 연결
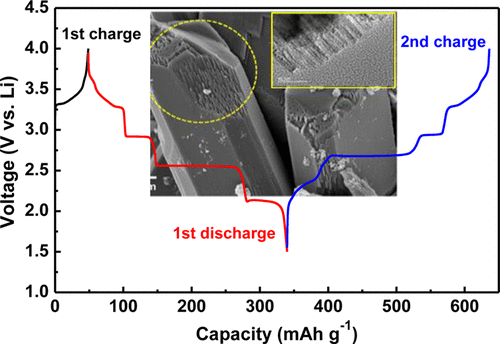
we prepared the LixV2O5 from electrochemical ion exchange of β-Na0.33V2O5, which is obtained by chemical conversion of NaVS2 in air at high temperatures. Crystal structure and particle morphology of β-Na0.33V2O5 are characterized by using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy techniques. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, in combination with electrochemical data, suggest that Na ions are extracted from β-Na0.33V2O5 without irreversible structural collapse and replaced with Li ions during the following intercalation (i.e., charging) process. The thus obtained LixV2O5 delivers a high discharge capacity of 295 mAh g–1, which corresponds to x = 2, with crystal structural stability in the voltage range of 1.5–4.0 V versus. Li, as evidenced by its good cycling performance and high Coulombic efficiency (under 0.1 mA cm–2) at room temperature. Furthermore, the ion-exchanged LixV2O5 from β-Na0.33V2O5 shows stable electrochemical behavior without structural collapse, even at a case of deep discharge to 1.5 V versus Li.