Electrochemical properties of a ceramic-polymer-composite-solid electrolyte for Li-ion batteries.
- Journal
- Solid State Ionics
- Vol
- 284
- Page
- 20-24
- Year
- 2016
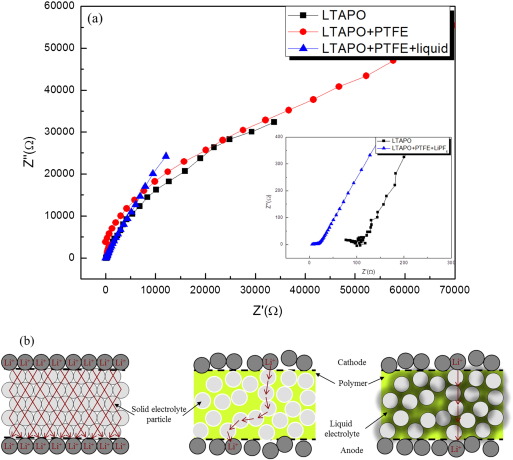
This study reports on the fabrication of a ceramic-polymer-composite electrolyte with liquid electrolyte, consisting of Li1.3Ti1.7Al0.3(PO4)3 (LTAPO) ceramic powder, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymer and 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC liquid electrolyte. The morphologies of the LTAPO, LTAPO–PTFE composite membrane, and LTAPO–PTFE–LiPF6–EC/DMC composite electrolyte were analyzed using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The effect of the liquid electrolyte on the ionic conductivity of the prepared ceramic-polymer electrolyte was investigated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The room temperature ionic conductivities of the LTAPO–PTFE–LiPF6–EC/DMC composite electrolyte and the LTAPO ceramic electrolyte exhibited 2.94 × 10− 4 S/cm and 8.36 × 10− 4 S/cm, respectively. The first charge capacity of the LTAPO–PTFE–LiPF6–EC/DMC composite electrolyte cell reached 118 mAh/g at 0.06 mA/cm2 current density. The electrochemical performance of the ceramic-polymer-composite electrolyte cell was better than that of the ceramic solid electrolyte cell.