Lithium ion dynamics in Li2S+GeS2+GeO2 glasses studied using 7Li NMR field-cycling relaxometry and line-shape analysis
- Journal
- Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
- Vol
- 70
- Page
- 53-62
- Year
- 2015
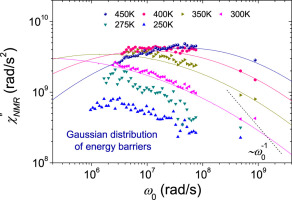
We use 7Li NMR to study the ionic jump motion in ternary 0.5Li2S+0.5[(1–x)GeS2+xGeO2] glassy lithium ion conductors. Exploring the “mixed glass former effect” in this system led to the assumption of a homogeneous and random variation of diffusion barriers in this system. We exploit that combining traditional line-shape analysis with novel field-cycling relaxometry, it is possible to measure the spectral density of the ionic jump motion in broad frequency and temperature ranges and, thus, to determine the distribution of activation energies. Two models are employed to parameterize the 7Li NMR data, namely, the multi-exponential autocorrelation function model and the power-law waiting times model. Careful evaluation of both of these models indicates a broadly inhomogeneous energy landscape for both the single (x=0.0) and the mixed (x=0.1) network former glasses. The multi-exponential autocorrelation function model can be well described by a Gaussian distribution of activation barriers. Applicability of the methods used and their sensitivity to microscopic details of ionic motion are discussed.