Sodium-ion Hybrid Electrolyte Battery for Sustainable Energy Storage Applications
- Journal
- Journal of Power Sources
- Vol
- 341
- Page
- 404-410
- Year
- 2017
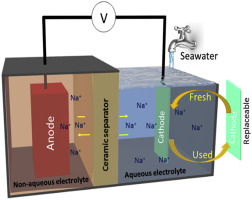
Sustainable, safe, and low-cost energy storage systems are essential for large-scale electrical energy storage. Herein, we report a sodium (Na)- ion hybrid electrolyte battery with a replaceable cathode system, which is separated from the Na metal anode by a Na superionic conducting ceramic. By using a fast Na-ion-intercalating nickel hexacyanoferrate (NiHCF) cathode along with an eco-friendly seawater catholyte, we demonstrate good cycling performance with an average discharge voltage of 3.4 V and capacity retention >80% over 100 cycles and >60% over 200 cycle. Remarkably, such high capacity retention is observed for both the initial as well as replaced cathodes. Moreover a Na-metal-free hybrid electrolyte battery containing hard ca bon as the anode exhibits an energy ~146 Wh kg-1 at a 10 mA g-1, which is comparable to that of batteries and much higher than that conventional aqueous Na-ion batteries. These results pave the way for further advances in sustainable energy storage technology.