LiCl-LiI molten salt electrolyte with bismuth-lead positive electrode for Liquid Metal Battery
- Journal
- Journal of Power Sources
- Vol
- 377
- Page
- 87-92
- Year
- 2018
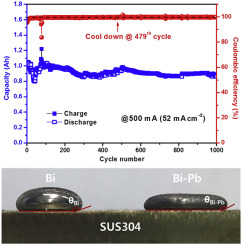
Liquid metal batteries (LMBs) are attractive energy storage device for large-scale energy storage system (ESS) due to the simple cell configuration and their high rate capability. The high operation temperature caused by high melting temperature of both the molten salt electrolyte and metal electrodes can induce the critical issues related to the maintenance cost and degradation of electrochemical properties resulting from the thermal corrosion of materials. Here, we report a new chemistry of LiCl-LiI electrolyte and Bi-Pb positive electrode to lower the operation temperature of Li-based LMBs and achieve the long-term stability. The cell (Li|LiCl-LiI|Bi-Pb) is operated at 410 ˚C by employing the LiCl-LiI (LiCl:LiI = 36:64 mol %) electrolyte and Bi-Pb alloy (Bi:Pb = 55.5:44.5 mol %) positive electrode. The cell shows excellent capacity retention (86.5 %) and high Coulombic efficiencies over 99.3 % at a high current density of 52 mA cm-2 during 1000th cycles.