Feasibility of using hollow double walled Mn2O3 nanocubes for hybrid Na-air battery
- Journal
- Chemical Engineering Journal
- Vol
- 360
- Page
- 415-422
- Year
- 2019
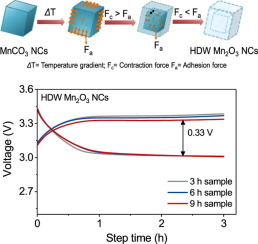
Synthesis of the strongly anisotropic materials, such as highly porous hollow double walled cubes are considered excellent approach to maximize the diffusion of electrolytes. Herein, hollow doubled walled (HDW) Mn2O3 nanocubes (NCs) were synthesized by facile hydrothermal method followed by calcination method. The growth of nanocubes were studied by performing hydrothermal reaction at different times ranging from 3 to 9 h. Thereafter, the feasibility of prepared HDW NCs as air cathode in hybrid Na-air battery was systematically investigated. Among all, the sample prepared by 9 h hydrothermal treatment showed superior performance than 3 and 6 h samples. The fabricated hybrid Na-air cell using HDW Mn2O3 NCs displayed 330 mV overpotential gap and 90% electrical energy efficiency at 5 mA g−1 current density, maximum of 0.2 W g−1 power density and good cyclic stability up to 75 cycles which is attributed to the highly porous nature of material that allows efficient diffusion of electrolyte ions and oxygen from air. Thus, present investigation suggests that HDW Mn2O3 NCs can be a potential air cathode and can be utilized in other metal-air battery systems.